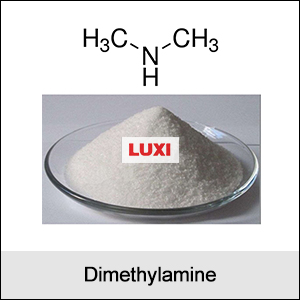
1. Properties of Dimethylamine:
- Chemical Formula: (CH₃)₂NH
- Molecular Weight: 45.08 g/mol
- Physical State: A colorless gas at room temperature with a strong, fishy odor. Often stored as a solution in water or other solvents.
- Boiling Point: 7°C (44.6°F)
- Melting Point: -92°C (-133.6°F)
- Density: Approximately 0.67 g/cm³ as a liquid.
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water and organic solvents.
2. Reactivity and Chemical Behavior:
- Basicity: A strong base due to the presence of the lone electron pair on nitrogen.
- Reactivity: Reacts with acids to form dimethylammonium salts. Undergoes alkylation and acylation reactions. Combustible in air, producing carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen oxides.
3. Applications of Dimethylamine:
- Chemical Synthesis: Precursor for the synthesis of agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and rubber accelerators. Used in the production of dimethylformamide (DMF) and dimethylacetamide (DMAc), key solvents in various industries.
- Agrochemical Industry: Used in the manufacture of herbicides, pesticides, and fungicides.
- Water Treatment: Utilized in the production of flocculants for water purification.
Pharmaceutical: Involved in synthesizing drugs such as antihistamines and local anesthetics.
4. Safety and Handling:
- Hazards:
- Flammability: Highly flammable in gaseous and liquid forms.
- Toxicity: May cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory system. Prolonged exposure can lead to more severe health effects.
- Corrosive: Can damage metals and some plastics.
- Protective Measures:
- Store and use in a well-ventilated area to prevent vapor accumulation.
- Use proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and a respirator.
- 5. Storage: Store in tightly sealed, corrosion-resistant containers in a cool, dry place away from heat or ignition sources.