Detail
1. Chemical Properties:
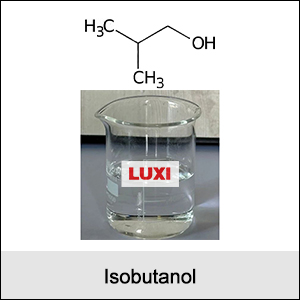
IUPAC Name: 2-Methylpropan-1-ol
Molar Mass: 74.12 g/mol
Structure:
Branched-chain alcohol with the functional group (-OH) attached to a carbon atom.
Appearance: Colorless liquid.
Odor: Characteristic alcoholic smell.
Boiling Point: 108 °C (226 °F).
Density: 0.802 g/cm³ at 20 °C.
Solubility: Miscible with organic solvents; moderately soluble in water.
2. Production:
Petrochemical Route:
Produced through the hydroformylation of propene to form isobutyraldehyde, followed by hydrogenation.
Biotechnological Route:
Can be produced through fermentation of biomass using engineered microorganisms.
3. Applications:
Solvent:
Used in paints, coatings, varnishes, and inks due to its ability to dissolve a wide range of compounds.
Fuel Additive:
Acts as an octane booster in gasoline blends and reduces engine knocking.
Chemical Intermediate:
Precursor for esters (e.g., isobutyl acetate) used in flavorings, perfumes, and solvents.
Industrial Uses:
Utilized in rubber, plastics, and synthetic resins manufacturing.
4. Health and Safety:
Toxicity:
Can cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract.
Inhalation of high concentrations can lead to dizziness, headaches, or nausea.
Flammability:
Highly flammable liquid and vapor with a flash point of 28 °C (82 °F).
Handling:
Use in well-ventilated areas with proper personal protective equipment (PPE).
Storage:
Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area away from sources of ignition.
5. Environmental Considerations:
Biodegradability:
Isobutanol is readily biodegradable and has low potential for bioaccumulation.
Emission Concerns:
Can contribute to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the atmosphere.